Resource Library
RMI: Clean Energy 101: Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal Heat Pumps: The Basics
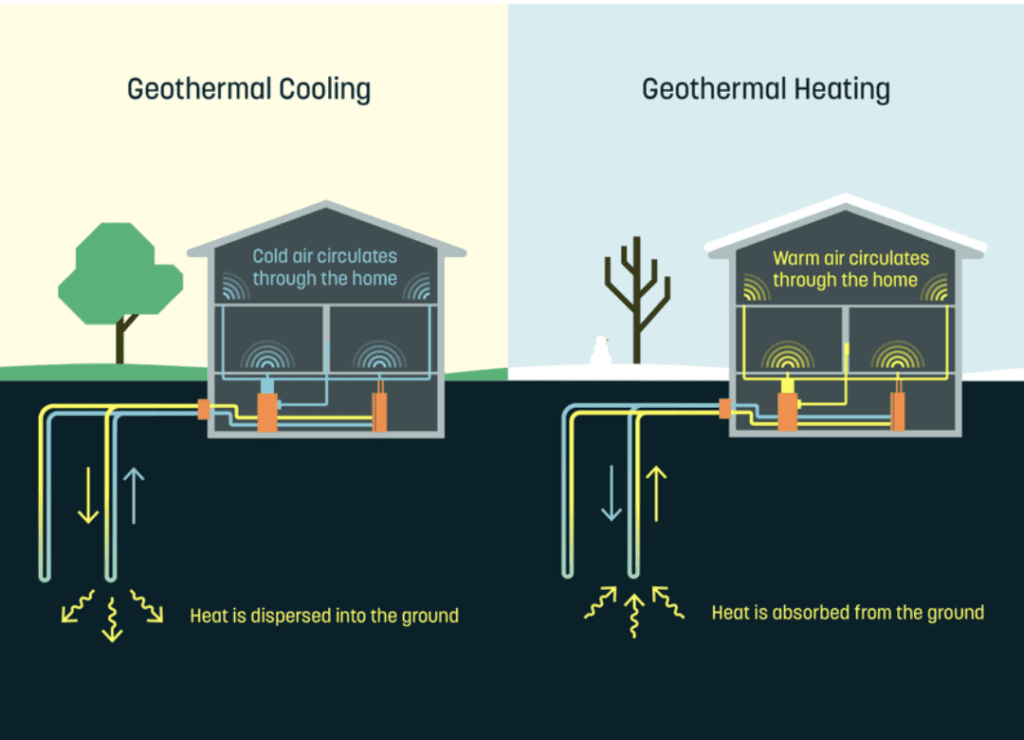
A geothermal heat pump is a clean, renewable technology that helps a home or building stay comfortable in any season. It harnesses the constant temperature below the earth’s surface to provide heating, cooling, and often hot water. Since geothermal is an abundant and renewable resource just beneath our feet, geothermal heat pumps are considered some of the most efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly HVAC and water-heating systems available. And because heat pumps simply move heat and don’t rely on combustion, like a gas furnace or water heater, they can reduce energy costs by up to 50 percent and produce zero direct emissions that contribute to air pollution and climate change.
Systems typically consist of a heat pump that replaces your furnace and is connected to pipes or a ground loop that contains heat-transferring liquid. These ground loops can be buried in horizontal trenches just below the earth’s surface or in deeper vertical boreholes, depending on location and density. The heat pump uses electricity to pull heat from the ground during colder months and works in reverse to dump heat into the ground when it’s hot out, acting as an air-conditioner. Conventional ductwork is most often used to distribute heated or cooled air from the heat pump throughout the building. Geothermal heat pumps are not geothermal power plants. Geothermal power plants produce electricity by using the heat underground to rotate a turbine, and they are primarily used for large-scale grid power, not connected homes and buildings.